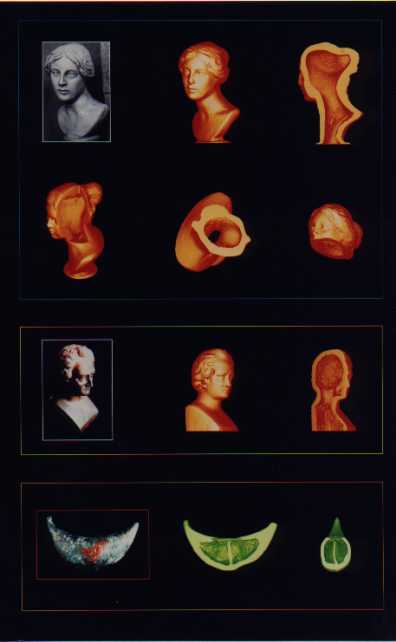
In the field of non destructive testings, computed tomography is one of the most advanced diagnostic techniques for its outstanding performance in showing the internal structures of the object under examination, see figures. It started in medical diagnosis, and now plays an important role in the industrial field. Recently, it has been used for the inspection of “cultural heritages” with encouraging results. An acquisition system, together with an image processing procedure, has been developed to perform “cone beam” tomographic investigations. Starting from digital radiographies acquired at different angles, it is possible to know the densitometric distribution of any slice of the object, and then to obtain a 3D reconstruction of the sample. When dealing with archeological samples, a good visualization of the internal structure of the object becomes of great importance to plan and realize a satisfying restoration.
A similar system has been set up in order to test the potentialities of neutron tomography. Originally developed for reactor fuel examination, this technique is now effective in detecting small corrosions and initial infiltrations of hydrogen or light materials within metallic structures, due to the particular behaviour of total neutron cross sections.