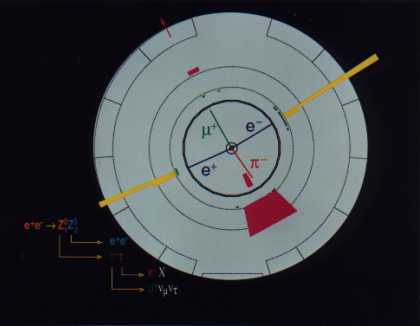
Particle theories describe the interactions between elementary particles via the exchange of mediators, called vector bosons. The photon plays the role of mediator for the electromagnetic interaction, while the Z0 boson is one of the mediators of the weak interaction. The Z0 decays almost immediately and only particles from the Z0 decay can be observed in the detectors.
The bottom figure shows the first “event” observed by the UA1 experiment, in which a Z0 boson is produced. The experiment, performed in 1983 by Carlo Rubbia and collaborators, was done at the proton-antiproton collider at CERN. The upper figure shows the first event e+e- Z0 Z0 charged leptons observed in 1997 at the electron-positron LEP collider at CERN. The positron is the anti-particle of the electron: the first Z0 decays into one electron and one positron (e-, e+) the second into two taus (t- ,t+); also the taus decay before reaching the detector, and only some of the particles produced in the decay are observed, in this case a muon m+ and a pion p-.
At LEP energies the weak and the electromagnetic interactions are unified into the electroweak interaction.
CERN, located in Geneva, Switzerland, is the largest particle physics laboratory.
