The 2020 FCC November week will take place online on November 9-13, 2020. The participation is open to all interested people.
Read more...
PageContent
RD-FCC
The label RD-FCC (RD-FA until July 2020) was created in 2017 to group together the various activities finalised to possible experiments at future accelerators or on future accelerator techniques.
The activities have focused on the study of a detector concept (IDEA) for a future circular electron-positron collider, and on the project of a muon collider.
IDEA
IDEA is an innovative general-purpose detector concept, designed to study electron-positron collisions in a wide energy range provided by a very large 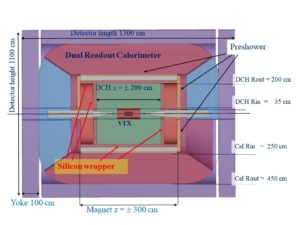 circular leptonic collider, with a circumference of 100 km. IDEA is a hermetic detector, geometrically subdivided in a cylindrical barrel region, closed at the extremities by two endcaps.
circular leptonic collider, with a circumference of 100 km. IDEA is a hermetic detector, geometrically subdivided in a cylindrical barrel region, closed at the extremities by two endcaps.
The detector is composed of the following sub detectors, in order of increasing distance from the primary vertex: a central tracking system composed of a vertex detector made of silicon pixel and strip detectors, and a large drift chamber with a 2m outer radius, providing more than 100 measurements along the track of every charged particle. The drift chamber also offers an excellent dE/dx measurement that leads to an outstanding particle identification. The central tracker is then completed by a silicon wrapper, made of silicon strip detectors, that surrounds the drift chamber. The central tracker is surrounded by a large but thin and low material solenoidal magnet that provides a 2 Tesla magnetic field. The solenoid is surrounded by the preshower detector. The preshower allows to identify and measure electromagnetic showers that originate in the material of the solenoid, before reaching the calorimeter. The preshower is constituted of a large array of a novel type of micro pattern gas detectors, the microRWELL. The preshower is followed by a dual readout (DR) calorimeter. The DR calorimeter has the particularity of measuring simultaneously the electromagnetic and hadronic component of the showers originated in the material of the calorimeter. It provides an excellent energy resolution, of the order of 30%/√E, on the measurement of hadronic jets. The electromagnetic energy resolution is of the order of 10%/√E, while maintaining a high granularity needed to disentangle two close-by showers originating from neutral pion decays. The last subdetector is the muon detection system. The muon detector uses the microRWELL technology, like the preshower, but with a coarser strip pitch. It is subdivided in three stations at increasing distance from the vertex, located within the iron return yoke that closes the magnetic field. Each muon station can provide a space point with a spatial resolution of about 400 microns in x-y coordinates. Combining the three stations allows to perform standalone tracking of charged particles at 5-6 m from the vertex. Such a precision also permits to identify secondary vertices that could be produced by long lived particles.
The IDEA detector concept was initially proposed by researchers from many INFN sections (Bari, Bologna, Ferrara, Lecce, LNF, Milano, Pavia, Pisa, Roma III and Torino). Afterwards, many foreign colleagues from many countries, like UK, France, Switzerland, Croazia, USA, Russia, South Korea and China have decided to collaborate.
FCC-ee
IDEA has been considered for, and is described in, the FCC Conceptual Design Report, published in January 2019, as a possible detector for one of the interaction regions of the CERN collider project, called FCC-ee, of a 100 km circumference e+e– collider, capable of operating at centre-of-mass energies ranging from 90 to 365 GeV, with an extremely high instantaneous luminosity, exceeding 1036 cm-2s-1 at the Z peak. Among the main characteristics of the FCC-ee collider is the possibility of studying with extraordinary precision the couplings of the Higgs boson, discovered in 2012 at the LHC.
as a possible detector for one of the interaction regions of the CERN collider project, called FCC-ee, of a 100 km circumference e+e– collider, capable of operating at centre-of-mass energies ranging from 90 to 365 GeV, with an extremely high instantaneous luminosity, exceeding 1036 cm-2s-1 at the Z peak. Among the main characteristics of the FCC-ee collider is the possibility of studying with extraordinary precision the couplings of the Higgs boson, discovered in 2012 at the LHC.
The FCC-ee collider will use the existing CERN accelerator complex as pre-accelerators before finally injecting the beams in the FCC 100 km long underground collider.
CepC
The IDEA detector has also been retained as a possible solution for one of 
the interacting regions of a competing project of a 100 km e+e– collider to be built in China, the CepC. The CepC will be built in a new Chinese laboratory and several possible locations are being considered. CepC would operate at centre-of-mass energies ranging from 90 to 240 GeV, with extremely high luminosities. Also the CepC collider will allow a great improvement on the measurements of the Higgs boson couplings to other particles, as well as measurements of the electroweak observables 20-50 times more precise compared to the LEP measurements obtained in the 90s.
The IDEA detector is described in the CepC Conceptual Design Report, published in late 2018.
Local responsible of RD-FA
Paolo Giacomelli
phone: 051-2095083
email: paolo.giacomelli@bo.infn.it














